0. 원문
교재 : Power electronIcs and motor drIves
1. 발췌
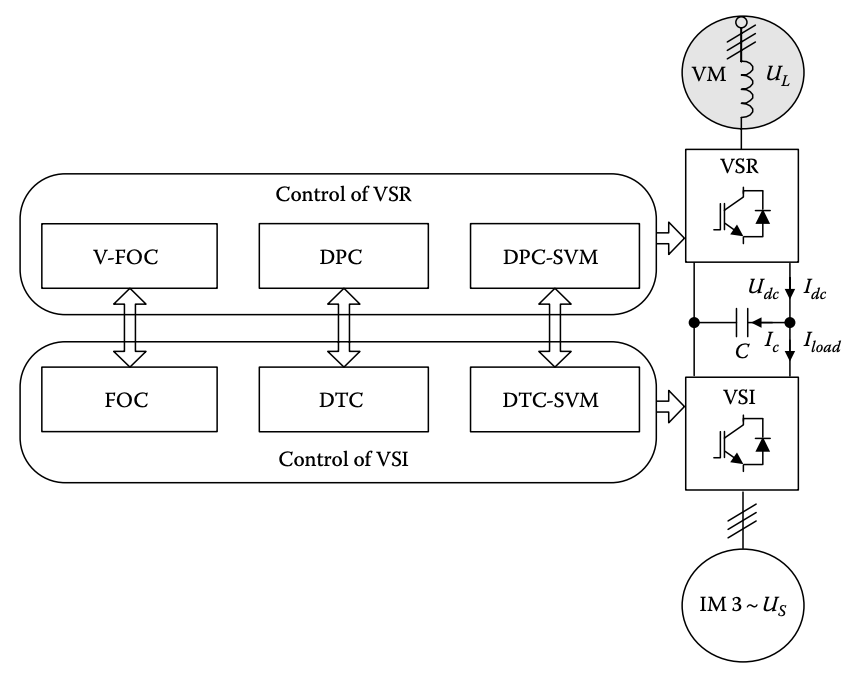
16.4 Vector Control Methods of AC–DC–AC Converter–Fed Induction Machine Drives: A Review

(1) 16.4.1 Field Oriented Control and Virtual Flux Oriented Control
VSI: The block diagram of the IFOC is presented in Figure 16.11. The commanded electromagnetic torque Mec, is delivered from outer PI speed controller, based on mechanical speed error e_Ωm.
VSI: IFOC의 블록 다이어그램은 Figure 16.11에 제시되어 있습니다. 명령된 전자기 토크 Mec는 외부 PI 속도 컨트롤러에서 제공되며, 이는 기계 속도 오차 e_Ωm을 기반으로 합니다.
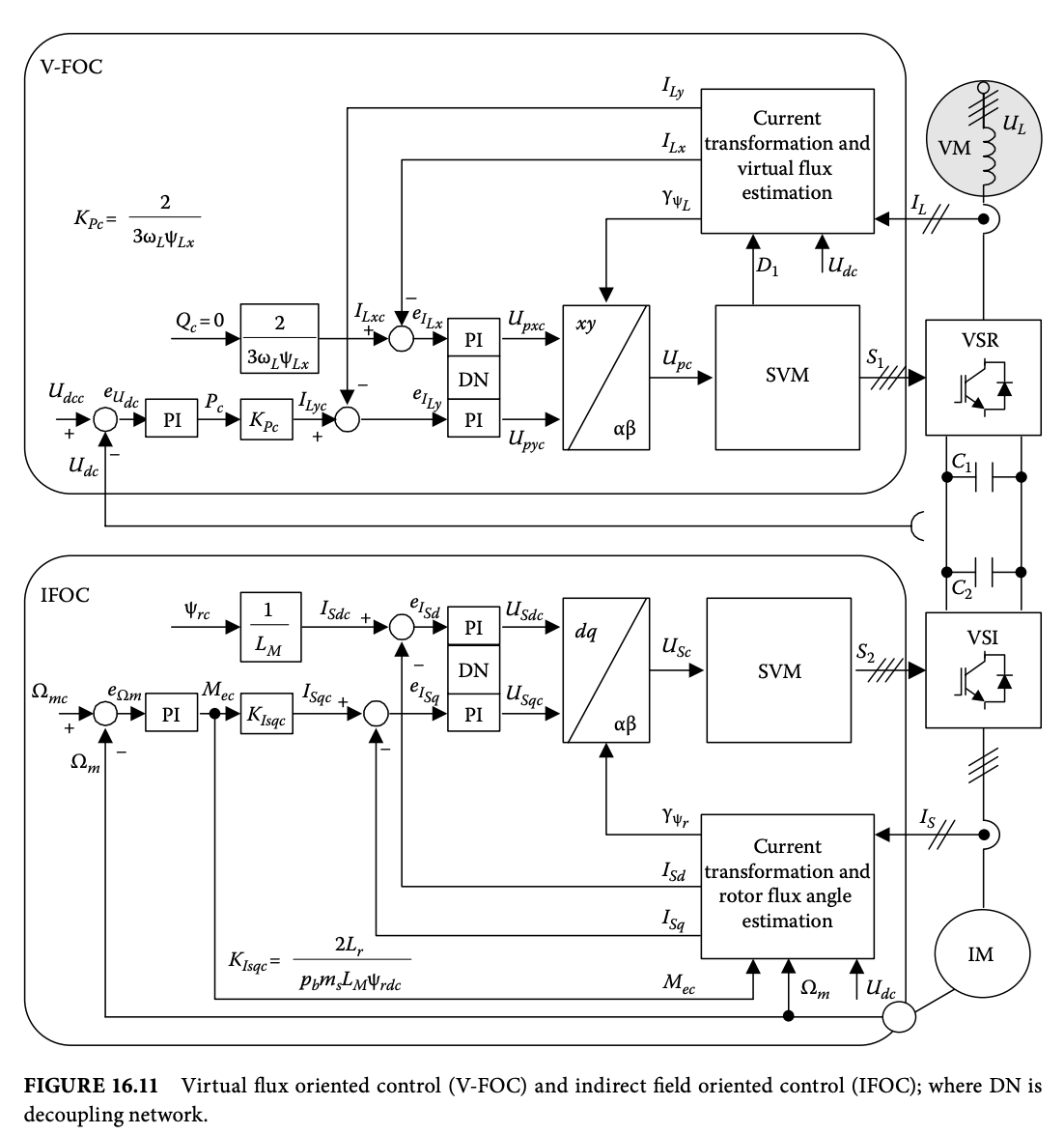
Then, command values ISdc and ISqc are compared with actual values of current component ISd and ISq, respectively. It should be stressed that (for steady state) ISd is equal to the magnetizing current, while the torque in both dynamic and steady states is proportional to ISq. The current errors eISd and eISq are fed to two PI controllers, which generate commanded stator voltage components USqc, and USdc, respectively. Further, commanded voltages are converted from rotating dq coordinates into stationary αβ coordinates using rotor flux vector position angle γΨr. So obtained voltage vector USc is delivered to space vector modulator (SVM), which generates appropriate switching states vector S2(S2A, S2B, S2C) for control power transistors of the VSI.
그런 다음, 명령 값 ISdc와 ISqc가 실제 전류 성분 ISd 및 ISq와 비교됩니다. 안정 상태에서 (steady state를 위해) ISd는 자화 전류와 동일하며, 동적 및 안정적인 상태에서 모든 토크는 ISq와 비례합니다. 전류 오차 eISd와 eISq는 두 개의 PI 컨트롤러로 전달되며, 각각 명령된 스테이터 전압 성분 USqc와 USdc를 생성합니다. 더 나아가, 명령된 전압은 로터 플럭스 벡터 위치 각도 γΨr를 사용하여 회전하는 dq 좌표에서 정지된 αβ 좌표로 변환됩니다. 이렇게 얻은 전압 벡터 USc는 공간 벡터 변조기(Space Vector Modulator, SVM)에 전달되며, VSI(Voltage Source Inverter)의 제어 전력 트랜지스터를 위한 적절한 스위칭 상태 벡터 S2(S2A, S2B, S2C)를 생성합니다.
VSR: VOC guarantees high dynamics and static performance via an internal current control loop. It has become very popular and has consequently been developed and improved. Therefore, VOC is a basis for V-FOC, which is shown in Figure 16.11. The goal of the control system is to maintain the DC-link voltage Udc, at the required level, while currents drawn from the power system should be sinusoidal like and in phase with line voltage to satisfy the UPF condition. The UPF condition is fulfilled when the line current vector IL = ILx + jILy, is aligned with the phase voltage vector UL = ULx + jULy, of the line. The idea of VF has been proposed to improve the VSR control under distorted and/or unbalanced line voltage conditions, taking the advantage of the integrator’s low-pass filter behavior [30]. Therefore, a rotating reference frame aligned with ΨL is used. The vector of VF lags the voltage vector by 90°. For the UPF condition, the command value of the direct component current vector ILxc is set to zero. Command value of the ILyc is an active component of the line current vector. After comparison, commanded currents with actual values, the errors are delivered to PI current controllers. Voltages generated by the controllers are transformed to αβ coordinates using VF position angle γΨL. Switching signal vector S1 for the VSR is generated by a space vector modulator.
VSR(Voltage Source Rectifier): VOC는 내부 전류 제어 루프를 통해 높은 다이내믹 및 정적 성능을 보장합니다. 이것은 매우 인기가 있으며 따라서 개발 및 개선되었습니다. 따라서 VOC는 Figure 16.11에 표시된 V-FOC의 기초입니다. 제어 시스템의 목표는 필요한 수준의 DC-링크 전압 Udc를 유지하면서 전원 시스템에서 뽑는 전류가 사인파 모양이고 선 전압과 위상이 일치하여 UPF(유니폼 파워 팩터) 조건을 충족시키는 것입니다. UPF 조건은 선 전류 벡터 IL = ILx + jILy가 선의 위상 전압 벡터 UL = ULx + jULy와 일치할 때 충족됩니다. VF의 아이디어는 VSR 제어를 왜곡되거나/또는 불균형된 선 전압 조건 하에서 개선하기 위해 제안되었으며, 통합기의 저패스 필터 특성을 활용합니다 [30]. 따라서 ΨL과 일치하는 회전 기준 프레임을 사용합니다. VF의 벡터는 전압 벡터를 90° 늦춥니다. UPF 조건을 위해 직류 성분 전류 벡터 ILxc의 명령값은 제로로 설정됩니다. ILyc의 명령값은 선 전류 벡터의 활성 성분입니다. 명령된 전류와 실제 값을 비교한 후, 오차는 PI 전류 컨트롤러로 전달됩니다. 컨트롤러에서 생성된 전압은 VF 위치 각도 γΨL을 사용하여 αβ 좌표로 변환됩니다. VSR에 대한 스위칭 신호 벡터 S1은 공간 벡터 변조기에 의해 생성됩니다.
(2) 16.4.2 Direct Torque Control and VF-Based Direct Power Control
VSI: The block diagram of the method is presented in Figure 16.12. The commanded electromagnetic torque Mec is delivered from outer PI speed controller. Then, Mec and commanded stator flux ΨSc amplitudes are compared with estimated values of Me and ΨS, respectively. The torque eM and flux eψ errors are fed to two hysteresis comparators
VSI (Voltage Source Inverter): 이 방법의 블록 다이어그램은 Figure 16.12에 제시되어 있습니다. 명령된 전자기 토크 Mec는 외부 PI 속도 컨트롤러에서 제공됩니다. 그런 다음, Mec와 명령된 스테이터 플럭스 ΨSc의 진폭은 각각 Me 및 ΨS의 추정값과 비교됩니다. 토크 오차 eM 및 플럭스 오차 eψ는 두 개의 히스테리시스 비교기(hysteresis comparators)에 전달됩니다.
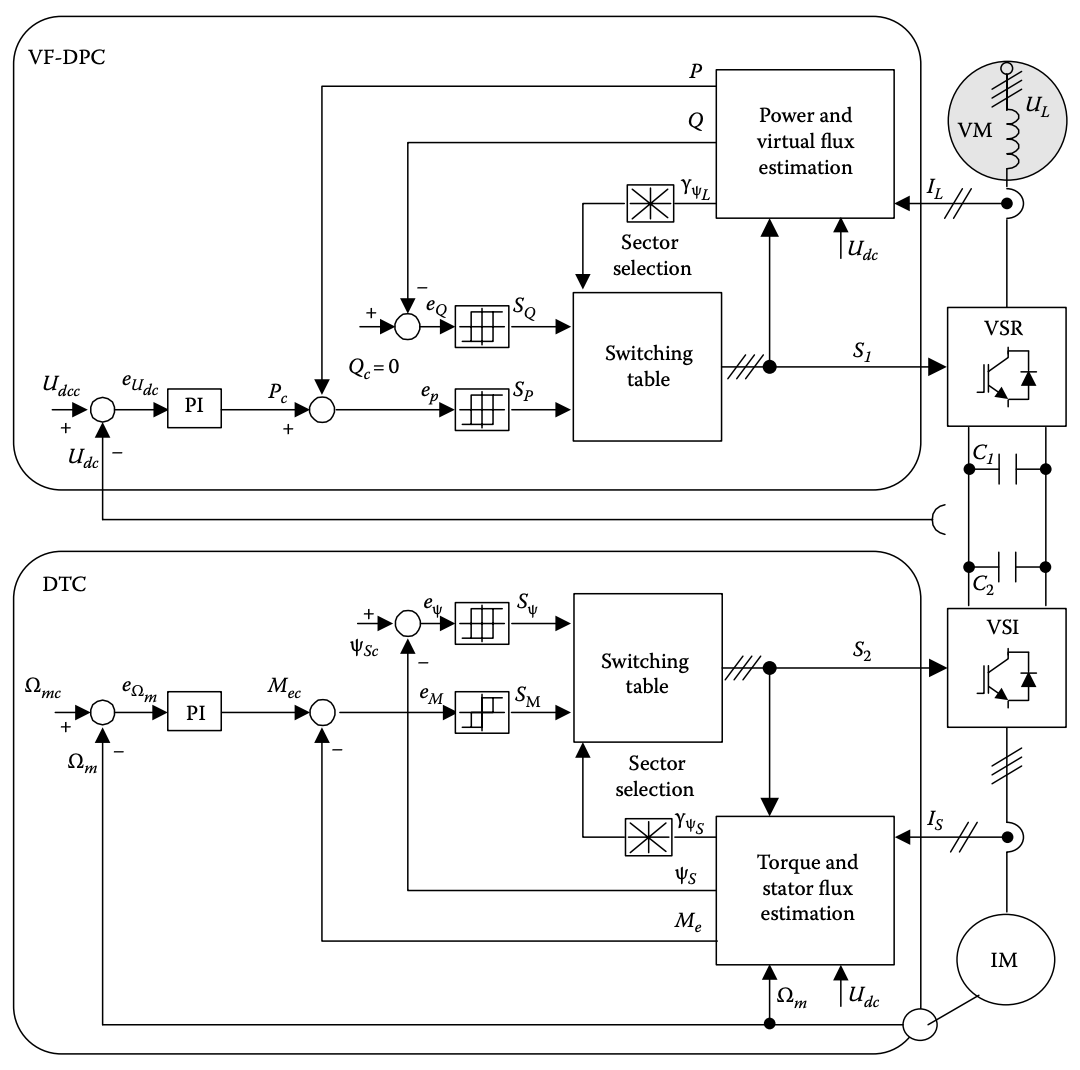
From predefined switching table, based on digitized error signals SM and SΨ, and the stator flux position γΨS the appropriate voltage vector is selected. The outputs from the predefined switching table are switching states S2 for the VSI. Then, voltage space vector plane for the DTC needs to be divided into six sectors as in Figure 16.12. The sectors could be defined in different manner [18].
미리 정의된 스위칭 테이블로부터, 디지털화된 오차 신호인 SM 및 SΨ, 그리고 스테이터 플럭스 위치 γΨS를 기반으로 적절한 전압 벡터가 선택됩니다. 미리 정의된 스위칭 테이블에서의 출력은 VSI를 위한 스위칭 상태 S2입니다. 그런 다음, DTC(Direct Torque Control)를 위한 전압 공간 벡터 평면은 Figure 16.12와 같이 여섯 개의 섹터로 나눠져야 합니다. 섹터는 다양한 방식으로 정의될 수 있습니다 [18].
'Study > Motor Control' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor(PMSM) modeling (0) | 2023.12.05 |
|---|---|
| SPMSM과 IPMSM 수식적 차이 비교 (0) | 2023.12.01 |
| 전기수중펌프(Electric submersible pump) (0) | 2023.09.28 |
| 적분기 누적 방지[Anti-Windup]기법 (0) | 2023.03.10 |
| IP 제어기[IP controller] (0) | 2023.03.08 |